Finding balance in our hormones is crucial for maintaining optimal health and well-being, especially for women. Hormonal equilibrium is responsible for regulating a wide range of bodily functions, including metabolism, sleep, mood, and reproductive health. However, imbalances in our hormones can lead to disruptions and unwanted symptoms. Nutrition plays a powerful role in supporting the body, but when it comes to balancing female hormones, it can be challenging to determine which foods are best for hormone balance. If you’re experiencing hormonal imbalance you are not alone — 80% of women will experience some form of hormonal imbalance at some point in their lives.
In this article, we will explore 12 hormone-balancing foods that every woman should consider incorporating into her diet. By understanding the impact of these foods on hormonal health, you can take proactive steps towards achieving and maintaining balance in your body.
1. Avocado
One of the best foods for balancing hormones is avocado. Packed with monounsaturated fatty acids, avocados are an excellent source of healthy fat that support mood and overall well-being. They are also rich in fiber, Potassium, Magnesium, Vitamin E, B Vitamins, and Folic Acid, making them a nutrient-dense addition to any diet.
How Does Avocado Help Balance Hormones?
Avocados play a significant role in balancing hormones due to their various beneficial properties. Research suggests that avocado intake is associated with improved glucose control and correction of insulin resistance, contributing to hormonal balance. They have also been found to increase estradiol and luteinizing hormone (LH) levels, supporting hormonal regulation. Because avocado is high in fiber, it is a great prebiotic, ultimately promoting a healthy gut microbiome and aiding in the removal of excess hormones. This nutrient dense fruit can also positively affect blood cholesterol levels and help balance cortisol, a stress hormone often at the root of many hormonal imbalances.
2. Berries
Berries, including blueberries, blackberries, raspberries, and strawberries, also offer hormone-balancing benefits. These fruits are high in Vitamin C, which acts as a powerful antioxidant. Antioxidants help protect the body's cells from damage caused by stress, promoting overall health. Packed with nutrients, berries are a fantastic addition to a hormone-balancing diet, providing a range of vitamins and phytochemicals that support hormonal health.
How Do Berries Help Balance Hormones?
Because berries are particularly rich sources of Vitamin C, they play a major role in hormone regulation. Research suggests that Vitamin C is involved in the regulation of progesterone levels and plays a crucial role in the menstrual cycle and ovarian function. Vitamin C levels shift throughout the menstrual cycle, declining before ovulation and increasing after post-ovulation temperature rise. Additionally, Vitamin C stimulates the production of progesterone and oxytocin — ultimately regulating menstrual cycle hormones. Berries also support metabolic health by reversing insulin resistance through sustaining healthy blood sugar levels, which can correct imbalanced hormones.
3. Cacao
Cacao, known for its rich and decadent flavor, offers more than just a delicious treat. It stimulates the release of endorphins, which are often referred to as the "feel-good" hormones, contributing to a brightened mood. Additionally, Cacao is packed with antioxidant properties, providing neural protection and promoting cognitive function. It is also an excellent source of Magnesium and Iron, both of which are essential for hormonal balance.
How Does Cacao Help Balance Hormones?
Cacao is known to help balance hormones and promote overall well-being. Its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, which are common side effects of imbalanced hormones in the body.
By improving mood and reducing stress, Cacao can alleviate some of the symptoms associated with hormone imbalance.
Additionally, Cacao is rich in Magnesium, a mineral that plays a crucial role in hormone regulation. High Magnesium levels can suppress the secretion of parathyroid hormones, further supporting healthy hormone levels for those experiencing thyroid issues. Don’t know how to add cacao into your diet? Our mushroom hot chocolate powder is bursting with beneficial ingredients like adaptogens and mushrooms, serving as the perfect morning beverage to start your day.
4. Cinnamon
Cinnamon is not only a flavorful spice but also a powerful ingredient for promoting balanced hormone levels. It contains essential minerals such as Calcium, Fiber, Iron, and Manganese. These nutrients play important roles in supporting various bodily functions, including hormone regulation. By incorporating cinnamon into your diet, you can benefit from its nutrition profile and support hormonal equilibrium.
How Does Cinnamon Help Balance Hormones?
Cinnamon is a natural ally for hormone balance. One of its key components is cinnamaldehyde, a natural chemical that has been found to have hormone-balancing effects. Cinnamaldehyde can increase the hormone progesterone while decreasing testosterone production in women, helping to restore hormonal balance. Cinnamon may also have promising effects in conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), as it has been shown to decrease luteinizing hormone (LH) and dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) levels and improve insulin resistance.
5. Cruciferous Vegetables
If you’re looking for foods that balance hormones in females, cruciferous vegetables is a great place to start. Cruciferous vegetables, such as broccoli, cauliflower, and brussels sprouts, are powerhouse foods packed with high nutritional value. Rich in vitamins C, E, and K, as well as Folate and fiber, these veggies are essential for digestive health and support optimal hormone function.
How do Cruciferous Vegetables Help Balance Hormones? H3
Cruciferous vegetables are one of the best foods for hormone balance because of their unique compounds and high fiber content. Research has shown that cruciferous vegetables contain compounds such as indole-3-carbinol (I3C) and diindolylmethane (DIM), which have a regulatory effect on estrogen. These compounds selectively bind to estrogen in the body, helping to maintain a healthy estrogen balance. Additionally, the high fiber content in cruciferous vegetables allows them to bind to excess hormones and facilitate their elimination from the body.
6. Coconut Oil
Coconut oil, with its rich content of fatty acids, including medium-chain fatty acids, is a valuable addition to a hormone-balancing diet. These fatty acids are easily digested and utilized by the body, providing a source of energy while supporting hormone production and regulation. Coconut oil is also a good source of Vitamin E and polyphenols, which have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. These properties help protect against oxidative stress and inflammation, both of which can negatively impact hormone balance.
How Does Coconut Oil Help Balance Hormones?
Coconut oil offers significant benefits for hormone balance by nourishing various systems in the body. Research suggests that coconut oil supports the immune system, gut health, and adrenal function, all of which play key roles in hormone health. It also has been found to have a preventive effect, particularly for pre-menopausal women, in maintaining hormonal balance. By incorporating coconut oil into your diet, you can provide essential support to these systems, promoting overall hormone health.
7. Green Tea
Green tea is known for its plethora of health benefits, particularly its ability to help balance hormones naturally. It’s a fantastic mineral-rich tea, high in Calcium, Chromium, Copper, Iron, Magnesium, Manganese, and Zinc, which are essential for hormone functionality.
How Does Green Tea Help Balance Hormones?
Green tea offers several mechanisms through which it helps to balance hormones. Research suggests green tea can enhance ovulation and reduce cyst formation in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a common hormonal disorder. It has also been found to reduce corticosterone levels, which are associated with adrenal hormone regulation. Green tea consumption has been linked to increases in follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and progesterone levels, both important for reproductive health. It also has powerful effects on fasting blood sugar and insulin levels, supporting metabolic health related hormone balance.
8. Leafy Greens
Leafy greens, such as spinach and kale, are nutritional powerhouses that contribute to hormone balance. Leafy greens are rich in antioxidants, helping to reduce oxidative stress. They’re also high in Vitamin A, Vitamin C, Vitamin K, Iron, Folate, and Potassium. These nutrients are crucial not only for hormone function but for overall health as well.
How Do Leafy Greens Help Balance Hormones?
Leafy greens help balance hormones thanks to their unique nutritional composition. Rich in antioxidants and fiber, leafy greens support hormone balance by reducing stress and increasing digestive health. These greens are also high in vitamin C, which has been shown to help reduce stress hormone levels and balance estrogen. Consuming leafy greens may reduce insulin resistance and testosterone, further supporting hormonal balance.
9. Lentils
Packed with antioxidants and fiber, lentils provide essential nutrients that support overall health and well-being. Their high fiber content aids in maintaining stable blood sugar levels, which is crucial for hormonal regulation. Lentils are also high in protein, making it a perfect choice for those seeking a plant-based, hormone-balancing protein source.
How Do Lentils Help Balance Hormones?
The combination of fiber and protein in lentils offers several hormonal benefits. The fiber content in lentils aids in reducing estrogen levels by binding to excess estrogen and promoting its elimination from the body. Simultaneously, the Zinc in lentils supports testosterone production. By including lentils in your diet, you can help regulate hormone levels, promote a healthy estrogen balance, and potentially increase testosterone levels.It is important to note, lentils should be avoided for those with PCOS as it can further imbalance testosterone levels.
10. Maca
Maca, a native Andean root, has been cultivated for thousands of years for its many health benefits. It has been traditionally used to support mood, energy levels, and healthy libido. Maca is a nutrient-dense food, rich in fiber, essential amino acids, fatty acids, and Copper, Iron, and Calcium. Maca root powder is often used in supplements to balance hormones.
How Does Maca Help Balance Hormones?
Maca has been shown to have hormone-balancing effects, particularly in menopausal women. Maca root for hormone balance can reduce the frequency and severity of individual menopausal symptoms while stimulating estrogen production and reducing follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) levels.
Maca has also been found to increase high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, also known as "good" cholesterol, which is important for metabolic health and ultimately balanced hormones.
11. Nuts
Nuts, such as Brazil nuts, almonds, and walnuts, are excellent additions to a hormone-balancing diet. Brazil nuts are particularly rich in Selenium, Magnesium, Copper, and Zinc, which are important minerals for supporting hormonal health. Almonds and walnuts, on the other hand, are packed with Vitamin E, Calcium, Phosphorus, and Folic Acid. These nutrients play various roles in hormone regulation.
How Do Nuts Help Balance Hormones?
Nuts can significantly improve hormone balance. Walnuts have been found to increase insulin response and sex hormone-binding globulin, which can contribute to hormone regulation. Almonds may also reduce androgen levels in women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Meanwhile, Brazil nuts have been shown to improve thyroid hormone levels because of their high Selenium content.
12. Seeds
Seeds, such as sesame, pumpkin, and flax seeds, offer immense benefits for hormone balance. These seeds are rich in healthy fats, including essential fatty acids, which are crucial for hormone production and regulation. These seeds are also excellent sources of Zinc, a mineral that plays a vital role in hormone synthesis. Consuming seeds can contribute to feelings of satiation and provide essential nutrients, making them an excellent addition to a hormone-balancing diet.
How Do Seeds Help Balance Hormones?
Seeds play a helpful role in balancing hormones due to their unique properties. Flaxseeds, known for their high content of lignans, have been shown to aid in the elimination of excess estrogen by binding to it. This can be beneficial for hormone balance, especially in conditions related to estrogen dominance. Pumpkin seeds, rich in zinc, support production of progesterone, an essential hormone for balancing estrogen levels, particularly during the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle when estrogen levels rise. Sesame seeds, high in Zinc and lignans, help block excess estrogen while progesterone rises. In postmenopausal women, sesame ingestion has been found to improve blood lipids, antioxidant status, and even sex hormones.
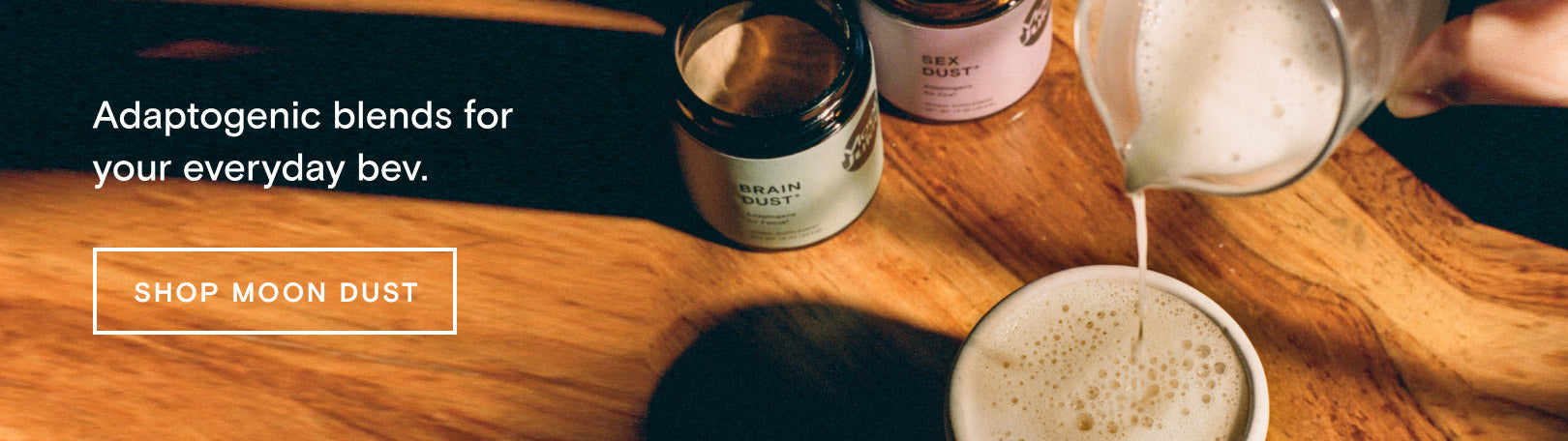
Sex Dust® for Hormone Balance
Supplementing your diet with herbs and adaptogens, in addition to a well-rounded and nutrient-dense hormone-balancing food diet, can provide further support for natural hormonal rebalancing. Take 1 tsp of Sex Dust® and add it to your daily coffee, tea, or smoothie to support hormonal balance and libido. Our natural hormone balance and libido supplement combines Shatavari root extract, Shilajit, Epimedium, Schisandra, Cacao, and Maca to target stress and aid in healthy hormone balance.*
Takeaways
Prioritizing hormonal balance is crucial for women's overall health and vitality. By making dietary changes, embracing these 12 foods to balance hormones and supplementing with hormone supportive herbs and adaptogen supplements, you can take proactive steps towards bringing your hormones back into balance and achieving optimal health. Remember, small changes in your diet can have a big impact on your hormonal well-being. Add these hormone-balancing foods to your diet today!

Sources
- National Library of Medicine, Avocado Consumption for 12 Weeks and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: A Randomized Controlled Trial in Adults with Overweight or Obesity and Insulin Resistance https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35700149/
- National Library of Medicine, Effects of Saturated Fat, Polyunsaturated Fat, Monounsaturated Fat, and Carbohydrate on Glucose-Insulin Homeostasis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomised Controlled Feeding Trials https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27434027/
- National Library of Medicine, Influence of ethanolic extract of avocado ( Persea americana Mill.) seed flour on the estrous cycle, the serum concentrations of reproductive hormones, and the activities of oxidative stress markers in female cavies ( Cavia porcellus L.) https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34722750/
- Harvard School of Public Health, Avocados https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/avocados/
- MDPI, Natural Molecules in the Management of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): An Analytical Review https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/13/5/1677
- National Library of Medicine, Dietary Vitamin C and Age-Induced Lipid and Hormonal Metabolic Changes in a Humanized Mouse Model Not Synthesizing Vitamin C and Producing Lipoprotein https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8221897/
- National Library of Medicine, Health benefits of cocoa https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24100674/
- National Library of Medicine, Magnesium and Human Health: Perspectives and Research Directions https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5926493/
- National Library of Medicine, Cinnamon and Chronic Diseases https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27771918/
- National Library of Medicine, The effect of cinnamon on polycystic ovary syndrome in a mouse model https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6194596/
- National Library of Medicine, The Potential of Cinnamon Extract (Cinnamomum burmanii) as Anti-insomnia Medication through Hypothalamus Pituitary Adrenal Axis Improvement in Rats https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36317999/
- National Library of Medicine, Cruciferous vegetables and human cancer risk: epidemiologic evidence and mechanistic basis https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17317210/
- National Library of Medicine, Health Effects of Coconut Oil-A Narrative Review of Current Evidence https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30395784/
- National Library of Medicine, Chemical composition and health benefits of coconut oil: an overview https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33022082/
- National Library of Medicine, Beneficial effects of green tea: A literature review https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2855614/
- National Library of Medicine, Beneficial Effects of Green Tea Catechins on Female Reproductive Disorders: A Review https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8124874/
- National Library of Medicine, The effects of spinach-derived thylakoid supplementation in combination with calorie restriction on anthropometric parameters and metabolic profiles in obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32782010/
- National Library of Medicine, Zinc status and serum testosterone levels of healthy adults https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8875519/
- National Library of Medicine, Polyphenol-Rich Lentils and Their Health Promoting Effects https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29125587/
- National Library of Medicine, Medicinal effects of Peruvian maca (Lepidium meyenii): a review https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31951246/
- National Library of Medicine, Hormone-Balancing Effect of Pre-Gelatinized Organic Maca (Lepidium peruvianum Chacon): (II) Physiological and Symptomatic Responses of Early-Postmenopausal Women to Standardized doses of Maca in Double Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Multi-Centre Clinical Study https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23675005/
- National Library of Medicine, Brazil nuts: Nutritional composition, health benefits and safety aspects https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28888463/
- National Library of Medicine, Differential effects of walnuts vs almonds on improving metabolic and endocrine parameters in PCOS https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21157477/
- National Library of Medicine, EFFECT OF SELENIUM SUPPLEMENTATION VIA BRAZIL NUT (BERTHOLLETIA EXCELSA, HBK) ON THYROID HORMONES LEVELS IN HEMODIALYSIS PATIENTS: A PILOT STUDY https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26545554/
- National Library of Medicine, Effect of flax seed ingestion on the menstrual cycle https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8077314/
- National Library of Medicine, Supplementation with flaxseed alters estrogen metabolism in postmenopausal women to a greater extent than does supplementation with an equal amount of soy https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14749240/
- National Library of Medicine, Effects of phytoestrogen extracts isolated from pumpkin seeds on estradiol production and ER/PR expression in breast cancer and trophoblast tumor cells https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23859042/
- National Library of Medicine, Sesame ingestion affects sex hormones, antioxidant status, and blood lipids in postmenopausal women https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16614415/